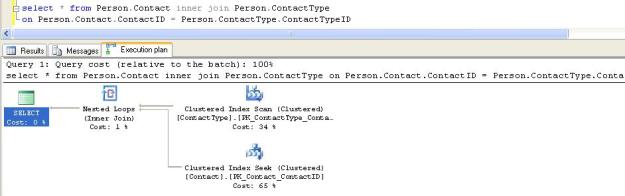
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP()
Returns the current database system timestamp as a datetime value without the database time zone offset.
GETDATE ()
Returns the current database system timestamp as a datetime value without the database time zone offset. This value is derived from the operating system of the computer on which the instance of SQL Server is running.
GETUTCDATE()
Returns the current database system timestamp as a datetime value. The database time zone offset is not included. This value represents the current UTC time (Coordinated Universal Time).
SYSDATETIME()
Returns a datetime2(7) value that contains the date and time of the computer on which the instance of SQL Server is running
SYSDATETIMEOFFSET()
Returns a datetimeoffset(7) value that contains the date and time of the computer on which the instance of SQL Server is running with timezone offset.
SYSUTCDATETIME
Returns a datetime2 value that contains the date and time of the computer on which the instance of SQL Server is running. The date and time is returned as UTC time (Coordinated Universal Time).
SELECT SYSDATETIME()
———————-
2011-01-10 06:38:25.05
SELECT SYSDATETIMEOFFSET()
———————————-
2011-01-10 06:38:25.0527369 -05:00
SELECT SYSUTCDATETIME()
———————-
2011-01-10 11:38:25.05
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
———————–
2011-01-10 06:38:25.050
SELECT GETDATE()
———————–
2011-01-10 06:38:25.050
SELECT GETUTCDATE()
———————–
2011-01-10 11:38:25.050
Note: Refer books online for more information.
18.520469
73.856621