Many times we want to restore the existing database or do DDL operation and often we are getting error Database is in use.
ALTER DATABASE databasename SET single_user WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
You required only DBO rights on the target database, even you don’t have sysAdmin rights it will work for that particular database.
Category Archives: SQL Server 2008
Scripts which make you Database Hero
— Create databsae SQLDBPool
CREATE DATABASE [sqldbpool] ON PRIMARY
( NAME = N’sqldbpool’, FILENAME = N’C:\sqldbpool.mdf’ , SIZE = 2048KB , MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED, FILEGROWTH = 1024KB )
LOG ON
( NAME = N’sqldbpool_log’, FILENAME = N’C:\sqldbpool_log.ldf’ , SIZE = 1024KB , MAXSIZE = 2048GB , FILEGROWTH = 10%)
COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
GO
–Script to create schema
USE [sqldbpool]
GO
CREATE SCHEMA [mySQLDBPool] AUTHORIZATION [dbo]
— Script to create table with constraints
create table mySQLDBPool.Emp
(
EmpID int Primary key identity(100,1),
EmpName Varchar(20) Constraint UK1 Unique,
DOB datetime Not Null,
JoinDate datetime default getdate(),
Age int Constraint Ck1 Check (Age > 18)
)
— Script to change the recovery model of the databsae
USE [master]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SQLDBPool] SET RECOVERY FULL WITH NO_WAIT
GO
ALTER DATABASE [SQLDBPool] SET RECOVERY FULL
GO
— Script to take the full backup of database
BACKUP DATABASE [SQLDBPool] TO DISK = N’D:\SQLDBPool.bak’
WITH NOFORMAT, INIT, NAME = N’SQLDBPool-Full Database Backup’,
NOREWIND, SKIP, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10
GO
–Script to take the Differential Database backup
BACKUP DATABASE [SQLDBPool] TO DISK = N’D:\SQLDBPool.diff.bak’
WITH DIFFERENTIAL , NOFORMAT, INIT, NAME = N’SQLDBPool-Diff Backup’,
NOREWIND, SKIP, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10
GO
–Script to take the Transaction Log backup that truncates the log
BACKUP LOG [SQLDBPool] TO DISK = N’D:\SQLDBPoolTlog.trn’
WITH NOFORMAT, INIT, NAME = N’SQLDBPool-Transaction Log Backup’,SKIP, NOREWIND, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10
GO
— Backup the tail of the log (not normal procedure)
BACKUP LOG [SQLDBPool] TO DISK = N’D:\SQLDBPoolLog.tailLog.trn’
WITH NO_TRUNCATE , NOFORMAT, INIT, NAME = N’SQLDBPool-Transaction Log Backup’,NOREWIND,SKIP, NOUNLOAD, NORECOVERY , STATS = 10
GO
— Script to Get the backup file properties
RESTORE FILELISTONLY FROM DISK = ‘D:\SQLDBPool.bak’
— Script to Restore Full Database Backup
RESTORE DATABASE [SQLDBPool1] FROM DISK = N’D:\SQLDBPool.bak’
WITH FILE = 1, MOVE N’sqldbpool’ TO N’D:\SQLDBPooldata.mdf’,
MOVE N’sqldbpool_log’ TO N’D:\SQLDBPoollog_1.ldf’,
NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10
GO
— Script to delete the backup history of the specific databsae
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_delete_database_backuphistory @database_name = N’SQLDBPool1′
GO
— Full restore with no recovery (status will be Restoring)
RESTORE DATABASE [SQLDBPool1] FROM DISK = N’D:\SQLDBPool.bak’
WITH FILE = 1, MOVE N’SQLDBPool’ TO N’D:\SQLDBPooldata.mdf’,
MOVE N’SQLDBPool_Log’ TO N’D:\SQLDBPoolLog_1.ldf’,
NORECOVERY, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10
GO
— Restore transaction log with recovery
RESTORE LOG [SQLDBPool1] FROM DISK = N’D:\SQLDBPoolLog.trn’
WITH FILE = 1, NOUNLOAD, RECOVERY STATS = 10
GO
–Script to bring the database online without restoring log backup
restore database sqldbpool with recovery
–Script to detach database
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_detach_db @dbname = N’SQLDBPool’
GO
— Script to get the database information
sp_helpdb ‘SQLDBPOOL’
–to Attach database
USE [master]
GO
CREATE DATABASE [SQLDBPool1] ON
( FILENAME = N’C:\SQLDBPool.mdf’ ),
( FILENAME = N’C:\SQLDBPool_Log.ldf’ )
FOR ATTACH
GO
USE SQLDBPool
GO
— Get Fragmentation info for each non heap table in SQLDBPool database
— Avg frag.in percent is External Fragmentation (above 10% is bad)
— Avg page space used in percent is Internal Fragmention (below 75% is bad)
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(dt.object_id) AS ‘Table Name’ , si.name AS ‘Index Name’,
dt.avg_fragmentation_in_percent, dt.avg_page_space_used_in_percent
FROM
(SELECT object_id, index_id, avg_fragmentation_in_percent, avg_page_space_used_in_percent
FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats (DB_ID(‘SQLDBPool’), NULL, NULL, NULL, ‘DETAILED’)
WHERE index_id <> 0) AS dt
INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS si
ON si.object_id = dt.object_id
AND si.index_id = dt.index_id
ORDER BY OBJECT_NAME(dt.object_id)
— Script to Get Fragmention information for a single table
SELECT TableName = object_name(object_id), database_id, index_id, index_type_desc, avg_fragmentation_in_percent, fragment_count, page_count
FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats (DB_ID(N’SQLDBPool’), OBJECT_ID(N’mySQLDBPool.Emp’), NULL, NULL , ‘LIMITED’);
–script to get the index information
exec sp_helpindex [mySQLDBPool.Emp]
–Script to Reorganize an index
ALTER INDEX PK_ProductPhoto_ProductPhotoID ON Production.ProductPhoto
REORGANIZE
GO
— Rebuild an index (offline mode)
ALTER INDEX ALL ON Production.Product
REBUILD WITH (FILLFACTOR = 80, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = ON,STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = ON);
–Script to find which columns don’t have statistics
SELECT c.name AS ‘Column Name’
FROM sys.columns AS c
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.stats_columns AS sc
ON sc.[object_id] = c.[object_id]
AND sc.column_id = c.column_id
WHERE c.[object_id] = OBJECT_ID(‘mySQLDBPool.Emp’)
AND sc.column_id IS NULL
ORDER BY c.column_id
— Create Statistics on DOB column
CREATE STATISTICS st_BirthDate
ON mySQLDBPool.Emp(DOB)
WITH FULLSCAN
— When were statistics on indexes last updated
SELECT ‘Index Name’ = i.name, ‘Statistics Date’ = STATS_DATE(i.object_id, i.index_id)
FROM sys.objects AS o WITH (NOLOCK)
JOIN sys.indexes AS i WITH (NOLOCK)
ON o.name = ‘Emp’
AND o.object_id = i.object_id
ORDER BY STATS_DATE(i.object_id, i.index_id);
— Update statistics on all indexes in the table
UPDATE STATISTICS mySQLDBPool.Emp
WITH FULLSCAN
— Script to shrink database
DBCC SHRINKDATABASE(N’SQLDBPool’ )
GO
— Shrink data file (truncate only)
DBCC SHRINKFILE (N’SQLDBPool_Data’ , 0, TRUNCATEONLY)
GO
— Script to shrink Shrink data file – Very Slow and Enhances the fragmentation
DBCC SHRINKFILE (N’SQLDBPool_Data’ , 10)
GO
— Script Shrink transaction log file
DBCC SHRINKFILE (N’SQLDBPool_Log’ , 0, TRUNCATEONLY)
GO
— Script to create view
CREATE VIEW emp_view
AS
SELECT *
FROM mySQLDBPool.emp
Central Management Server
Central Management Server
SQL Server Central Management Server is just a central repository that holds a list of managed servers. Microsoft has introduced CMS feature in SQL Server 2008 SSMS.
Use of Central Management Server
1. Multiple Server Query Execution, we can execute query against multiple servers and get the result at source.
2.Centralize the management and administration of a number of SQL Server instances from a single source can allow the DBA to save significant time and effort.
3.Evaluate policy against the multiple server from single source.
4.Control Services and bring up SQL Server Configuration Manager
5.Import and export the registered servers:
Pre-requisite:
You must have at least 1 SQL Server 2008 instance which can be used as CMS
Steps to Create CMS and Register Server
1. Open the “Registered Servers” from the “View” Menu in the management studio of SQL server 2008.
2. Right click on the Central Management Servers and select “Register Central Management Server” and Register the SQL Server 2008 instance as CMS.
3. Create the groups under Registered CMS servers to define the group for each server.
4. Right Click on groups and register the all the SQL Server instances as per their group. (SQL Server 2000,2005 and 2008)
SQL Profiler
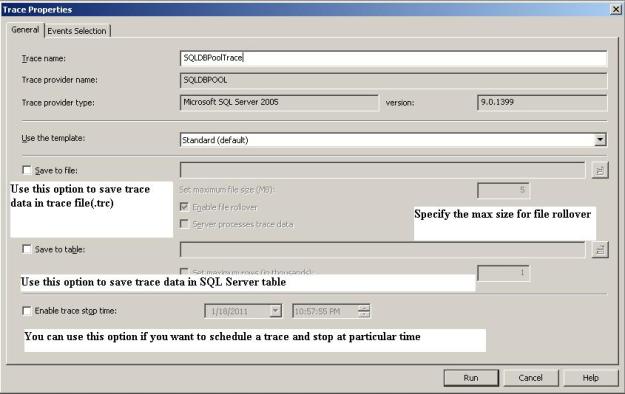
SQL Server Profiler is a graphical tool that helps in the monitoring of an instance of SQL Server Database Engine or Analysis Services. SQL Profiler is a tool which monitors the events and activity running on a SQL Server instance. The results can be saved to a file or inside a SQL Server table. We can replay this saved trace. Profiler is mostly used in stress testing a server, analyzing performance, debugging TSQ statements, and auditing SQL Server activity.
See below image to see how to open SQL Profiler

See below list for the Key terms associated with profiler.
Event is an action that is generated within an instance of a SQL Server Database Engine. These could be login failure, connection failure or any disconnection. It will include events such as T-SQL statements, remote procedure call batch status, the start or end of a stored procedure, the start or end of statements within a stored procedure and so on.. These are displayed in the trace in a single row intersected by data columns with descriptive details.
Event Class is an event that can be traced and contains all of the data that can be reported by the event. For example SQL: Batch completed for instance is an event class
Event Category defines the methodology used for grouping events within the SQL Server Profiler. For instance lock events will be categorized under Lock event category.
Data Column is an attribute of an event class that is captured in the trace.
Template is the default configuration for a trace. It includes the event classes that are required for monitoring.
Trace captures data based on selected event classes, data columns and filters.
Filter Data can be filtered by specifying criteria of selection during the execution of an event. This feature is used to reduce the size of the Trace.
You can use fn_trace_gettable function to read the trace file.
SQL Server Services
As per the options you choose during the SQL Server installation, it will install below services on server.
SQL Server Database Services – The service is used for SQL Server relational Database Engine.
SQL Server Agent – is used for scheduling. It executes jobs, monitors SQL Server, send alerts, and enables automation of some of the administrative tasks.
Analysis Services – Provides online analytical processing (OLAP) and data mining functionality for business intelligence applications.
Reporting Services – Manages, executes, creates, schedules, and delivers reports.
Integration Services –is used for SSIS package. It provides management support for Integration Services package storage and execution.
SQL Server Browser – The name resolution service that provides SQL Server connection information for client computers. It is used for named instance only.
Full-text search – Provided full text index and searching facility for BLOB columns.
SQL Server Active Directory Helper – Publishes and manages SQL Server services in Active Directory.
SQL Writer – Allows backup and restore applications to operate in the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) framework.