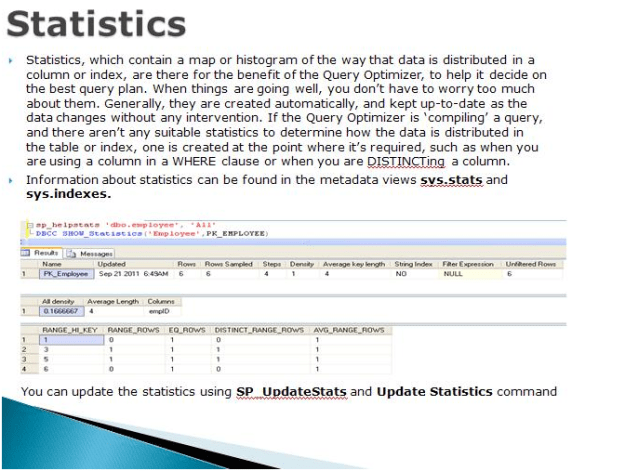
Script to find out the statistics update date for all the indexes in the current database
sp_MSforeachtable 'sp_autostats "?"'
Script to update the statistics of all the indexes
EXEC sp_MSforeachtable 'UPDATE STATISTICS ? WITH FULLSCAN'
Script to find out the statistics update date for all the indexes in the current database
sp_MSforeachtable 'sp_autostats "?"'
Script to update the statistics of all the indexes
EXEC sp_MSforeachtable 'UPDATE STATISTICS ? WITH FULLSCAN'

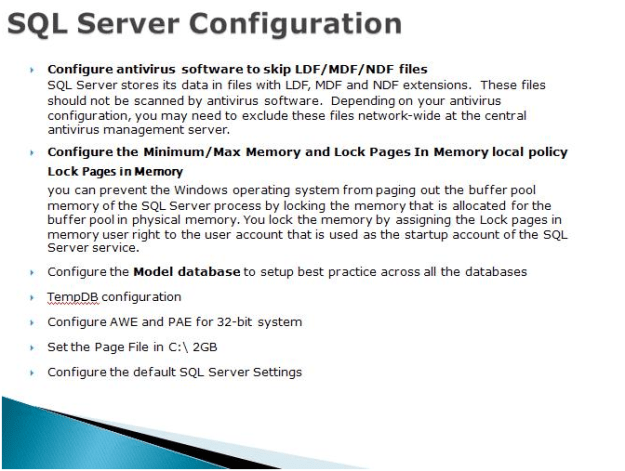
Lock Pages in Memory
You can prevent the Windows operating system from paging out the buffer pool memory of the SQL Server process by locking the memory that is allocated for the buffer pool in physical memory. You lock the memory by assigning the Lock pages in memory user right to the user account that is used as the startup account of the SQL Server service.
Model Database Whenever we create a new database, it will use model as template. Configure model DB for the Auto Shrink OFF, Auto Update/Create Statistics on
Maximum Worker Threads: Based on the load increase the maximum work thread.
Address Windowing Extensions (AWE) is an API that allows a 32-bit application to manipulate physical memory beyond 4 GB memory limit. The AWE mechanism technically is not necessary on 64-bit platform. It is, however, present there. Memory pages that are allocated through the AWE mechanism are referred as locked pages on the 64-bit platform.
On both 32-bit and 64-bit platforms, memory that is allocated through the AWE mechanism cannot be paged out. This can be beneficial to the application. (This is one of the reasons for using AWE mechanism on 64-bit platform.) This also affects the amount of RAM that is available to the system and to other applications, which might have detrimental effects. For this reason, in order to use AWE, the Lock Pages in Memory privilege must be granted for the account that runs SQL Server.

Please note:

 .
.