DAC: Dedicated Administrator Connection feature is available from the SQL Server 2005. It is available in all the higher editions by default except express edition. DAC will be useful when SQL Server is not responding any connections; in such kind of situation DBA will connect through the DAC and troubleshoot/fix the issue.
You can execute below kind of command for the initial troubleshooting.
-- Locking Info
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_tran_locks
GO
-- Running Sessions
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_exec_sessions
GO
-- Requests Status
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_exec_requests
GO
--Open Sessions
SP_WHO2
--To get the SQL Text
DBCC OPENTRAN (SPID)
--To terminate the curlprit process
KILL SPID
DAC is disabled by default, it is a good practice to enable the DAC. You can enable the DAC using by executing below query.
Use master
GO
--0 = Allow Local Connection,
--1 = Allow Remote Connections*/
sp_configure 'remote admin connections', 1
GO
RECONFIGURE
GO
You can connect using DAC on of the following method.
Command Prompt
SQL Server Management Studio
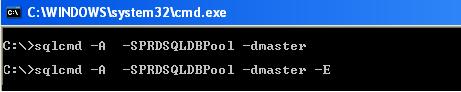
Using Command Prompt: Use SQLCMD utility to connect to SQL Server as below.
-A argument is to specify the DAC connection.
-S argument is to specify the server name.
-d argument is to specify the database name.
-E argument is for windows connection with integrated security true
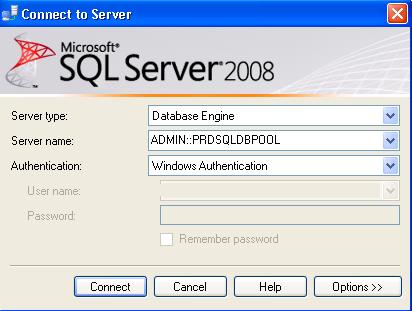
Using Management Studio: Write ADMIN: before the server name in management studio connection window. It will give you the DAC connection.
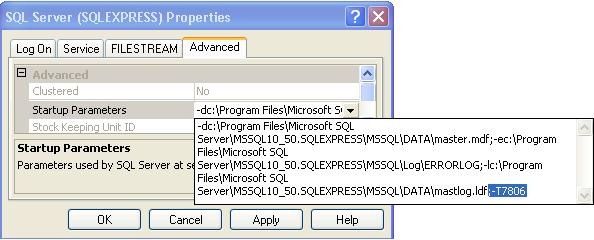
To enable the DAC connection in SQL Server express edition add ;-T7806 trace flag as startup parameter.
Go into configuration manager — right click on SQL Server Service and select properties — go into advanced tab and add the trace flag ;-T7806. Once done restart the SQL Server Services.
18.520469
73.856621