Recently I got a requirement to drop all SQL Logins from the SQL Server. I have created below script to drop all SQL Login.
Before getting into detail, please take a note that “A login cannot be dropped while it is logged in. A login that owns any securable, server-level object, or SQL Server Agent job cannot be dropped”
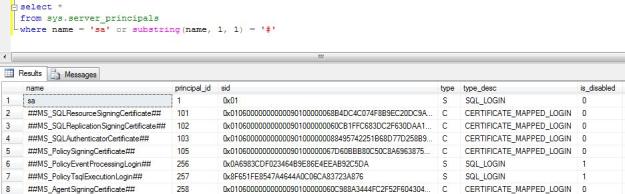
SA login account and the few policy certificates also come in SQL Login type, I have excluded them.
select * from sys.server_principals where name = 'sa' or substring(name, 1, 1) = '#'
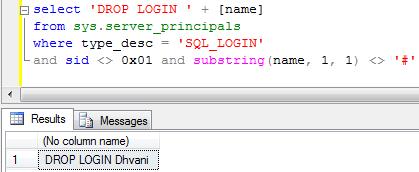
select 'DROP LOGIN ' + [name] from sys.server_principals where type_desc = 'SQL_LOGIN' and sid <> 0x01 and substring(name, 1, 1) <> '#'
Next step is to execute the output of the above query.