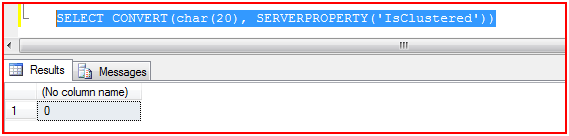
A deadlock occurs when two or more processes permanently block each other by each process having a lock on a resource which the other process are trying to lock.
Please execute the below queries as per the mentioned comments to produce a deadlock.
--turning on the traceflag to record deadlock info into error log
dbcc traceon(1204,-1)
dbcc tracestatus(1204)
--creating test database
create database sqlDBPool
--Connecting to SQLDBPool database
use sqldbpool
--table creation
create table tb1 (col1 int)
create table tb2 (col1 int)
--inserting dummy records
insert into tb1 values(1),(2),(3)
insert into tb2 values(1),(2),(3)
--Open first connection to update table explicit transaction
begin transaction
update tb1 set col1 = 5
--Open second connection to update table explicit transaction
use sqlDBPool
begin transaction
update tb2 set col1 = 6
update tb1 set col1 = 6
--Open first connection to update table explicit transaction
update tb2 set col1 = 5
You can see the one of the transaction will fail with the below error message.
Msg 1205, Level 13, State 45, Line 3
Transaction (Process ID 55) was deadlocked on lock resources with another process and has been chosen as the deadlock victim. Rerun the transaction.
As we have turned on the deadlock trace flag, you can see the below information in the SQL Server error log.
Starting up database 'sqlDBPool'.
Deadlock encountered .... Printing deadlock information
Wait-for graph
NULL
Node:1
RID: 9:1:153:0 CleanCnt:2 Mode:X Flags: 0x3
Grant List 1:
Owner:0x05684480 Mode: X Flg:0x40 Ref:0 Life:02000000 SPID:52 ECID:0 XactLockInfo: 0x065F82A8
SPID: 52 ECID: 0 Statement Type: UPDATE Line #: 1
Input Buf: Language Event: update tb2 set col1 = 5
Requested by:
ResType:LockOwner Stype:'OR'Xdes:0x05A8CC10 Mode: U SPID:55 BatchID:0 ECID:0 TaskProxy:(0x05A70354) Value:0x6767b20 Cost:(0/432)
NULL
Node:2
RID: 9:1:155:0 CleanCnt:2 Mode:X Flags: 0x3
Grant List 2:
Owner:0x067679A0 Mode: X Flg:0x40 Ref:0 Life:02000000 SPID:55 ECID:0 XactLockInfo: 0x05A8CC38
SPID: 55 ECID: 0 Statement Type: UPDATE Line #: 3
Input Buf: Language Event: begin transaction update tb2 set col1 = 6 update tb1 set col1 = 6
Requested by:
ResType:LockOwner Stype:'OR'Xdes:0x065F8280 Mode: U SPID:52 BatchID:0 ECID:0 TaskProxy:(0x0941A354) Value:0x6a943a0 Cost:(0/432)
NULL
Victim Resource Owner:
ResType:LockOwner Stype:'OR'Xdes:0x05A8CC10 Mode: U SPID:55 BatchID:0 ECID:0 TaskProxy:(0x05A70354) Value:0x6767b20 Cost:(0/432)