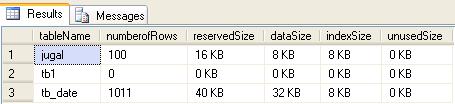
Today I received an email from my one of blog reader regarding identification of different objects using Sys.sysObjects.
You can query the sys.SysObjects to get all the objects created with in the database.
Example
SELECT *
FROM sys.sysobjects
WHERE TYPE = ‘u’
Below are the different kind of object you can retrieve from database.
Object Type Abbreviation
AF = Aggregate function (CLR)
C = CHECK constraint
D = Default or DEFAULT constraint
F = FOREIGN KEY constraint
L = Log
FN = Scalar function
FS = Assembly (CLR) scalar-function
FT = Assembly (CLR) table-valued function
IF = In-lined table-function
IT = Internal table
P = Stored procedure
PC = Assembly (CLR) stored-procedure
PK = PRIMARY KEY constraint (type is K)
RF = Replication filter stored procedure
S = System table
SN = Synonym
SQ = Service queue
TA = Assembly (CLR) DML trigger
TF = Table function
TR = SQL DML Trigger
TT = Table type
U = User table
UQ = UNIQUE constraint (type is K)
V = View
X = Extended stored procedure