If you don’t remember all the DBCC commands “NO Issue” execute the DBCC HELP command to get the list of all the DBCC.
DBCC HELP('?')
checkalloc
checkcatalog
checkconstraints
checkdb
checkfilegroup
checkident
checktable
cleantable
dbreindex
dropcleanbuffers
free
freeproccache
freesessioncache
freesystemcache
help
indexdefrag
inputbuffer
opentran
outputbuffer
pintable
proccache
show_statistics
showcontig
shrinkdatabase
shrinkfile
sqlperf
traceoff
traceon
tracestatus
unpintable
updateusage
useroptions
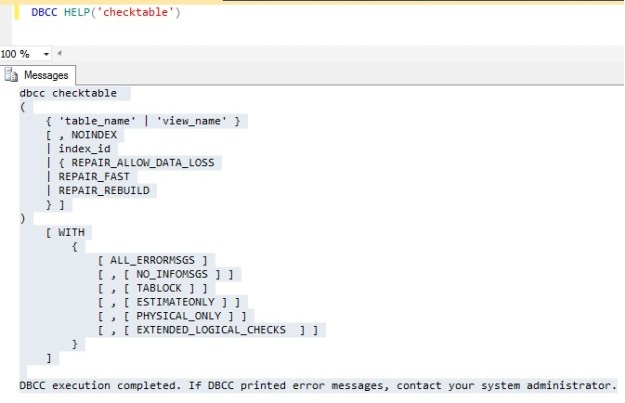
DBCC execution completed. If DBCC printed error messages, contact your system administrator.
Don’t remember syntax, execute below command to get the syntax.
DBCC HELP('checktable')