sys.dm_os_ring_buffers: You can use the undocumented Ring Buffer DMV to troubleshoot the below issues.
- Security Exceptions
- Exception raised at SQL Operating System level
- Connection Dropped By the Server
- System Resource Utilization
- Memory Pressure
- CLR Integration Scheduler State
- Extended Events Subsystems State
Execute the below query to get the distinct ring buffer type.
select distinct ring_buffer_type from sys.dm_os_ring_buffers
- RING_BUFFER_RESOURCE_MONITOR
- RING_BUFFER_SCHEDULER_MONITOR
- RING_BUFFER_MEMORY_BROKER
- RING_BUFFER_SECURITY_ERROR
- RING_BUFFER_XE_BUFFER_STATE
- RING_BUFFER_SCHEDULER
- RING_BUFFER_CONNECTIVITY
- RING_BUFFER_EXCEPTION
- RING_BUFFER_XE_LOG
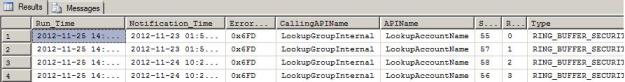
Check below script as example to troubleshoot the Security Issue using ring buffer. You can change the ring buffer type in below script to troubleshoot the different issues.
-- Check the Ring Buffer in SQL Server 2008
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
SET ANSI_WARNINGS ON
SET ANSI_PADDING ON
SELECT CONVERT (varchar(30), GETDATE(), 121) as Run_Time,
dateadd (ms, (ST.[RecordTime] - sys.ms_ticks), GETDATE()) as [Notification_Time],
ST.* , sys.ms_ticks AS [Current Time]
FROM
(SELECT
RBXML.value('(//Record/Error/ErrorCode)[1]', 'varchar(30)') AS [ErrorCode],
RBXML.value('(//Record/Error/CallingAPIName)[1]', 'varchar(255)') AS [CallingAPIName],
RBXML.value('(//Record/Error/APIName)[1]', 'varchar(255)') AS [APIName],
RBXML.value('(//Record/Error/SPID)[1]', 'int') AS [SPID],
RBXML.value('(//Record/@id)[1]', 'bigint') AS [Record Id],
RBXML.value('(//Record/@type)[1]', 'varchar(30)') AS [Type],
RBXML.value('(//Record/@time)[1]', 'bigint') AS [RecordTime]
FROM (SELECT CAST (record as xml) FROM sys.dm_os_ring_buffers
WHERE ring_buffer_type = 'RING_BUFFER_SECURITY_ERROR') AS RB(RBXML)) ST
CROSS JOIN sys.dm_os_sys_info sys
ORDER BY ST.[RecordTime] ASC
-- Script to Check the Ring Buffer in SQL Server 2005
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
SET ANSI_WARNINGS ON
SET ANSI_PADDING ON
SELECT CONVERT (varchar(30), GETDATE(), 121) as runtime,
DATEADD (ms, -1 * ((sys.cpu_ticks / sys.cpu_ticks_in_ms) - ST.[RecordTime]), GETDATE()) AS NotificationTime,
ST.* , sys.ms_ticks AS [CurrentTime]
FROM
(SELECT
RBXML.value('(//Record/Error/ErrorCode)[1]', 'varchar(30)') AS [ErrorCode],
RBXML.value('(//Record/Error/CallingAPIName)[1]', 'varchar(255)') AS [CallingAPIName],
RBXML.value('(//Record/Error/APIName)[1]', 'varchar(255)') AS [APIName],
RBXML.value('(//Record/Error/SPID)[1]', 'int') AS [SPID],
RBXML.value('(//Record/@id)[1]', 'bigint') AS [Record Id],
RBXML.value('(//Record/@type)[1]', 'varchar(30)') AS [Type],
RBXML.value('(//Record/@time)[1]', 'bigint') AS [RecordTime]
FROM (SELECT CAST (record as xml) FROM sys.dm_os_ring_buffers
WHERE ring_buffer_type = 'RING_BUFFER_SECURITY_ERROR') AS RB(RBXML)) ST
CROSS JOIN sys.dm_os_sys_info sys
ORDER BY ST.[RecordTime] ASC
From the output we can see the hexadecimal error code 0x6FD. You have to convert these error code into decimal value, which will be 0x6FD = 1789
Check the above decimal error codes using the NET HELPMSG command, which will give you more information on the issue.